
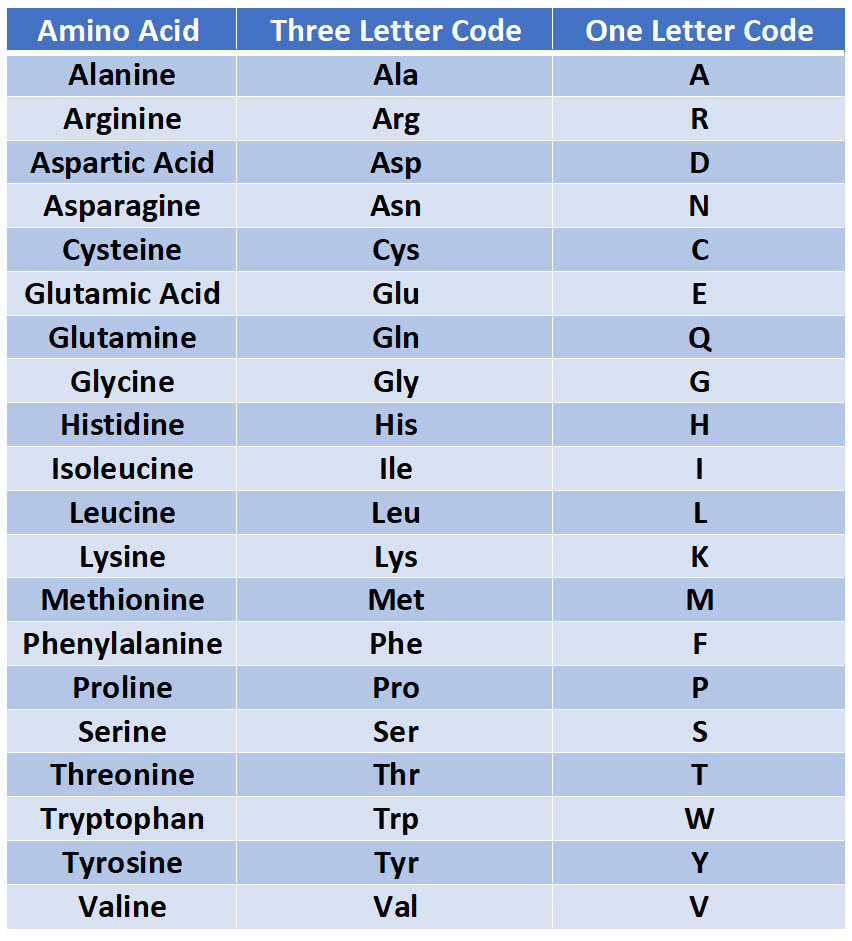
Treatment of the original peptide with the enzyme carboxypeptidase released cysteine. The polymerized hemoglobin distorts red blood cells into an abnormal sickle shape. This creates a new hydrophobic spot (shown white). Suppose that treatment of the intact peptide with the enzyme aminopeptidase released valine. Sickle hemoglobin differs from normal hemoglobin by a single amino acid: valine replaces glutamate at position 6 on the surface of the beta chain. The amino terminal is converted from a positive to a negative charge favouring salt bridge formation between the a and P chains. The small energies responsible for small molecule. If you were a graduate student faced with such a challenge, you might subject some of your white powder sample to acid hydrolysis and find that the following amino acids were present: Hemoglobin can bind CO, directly when oxygen is released and CO, reacts with the amino terminal a-amino groups of the hemoglobin forming a carbamate and releasing protons. These are not unique, because hundreds of amino acids are involved in allosteric strain fields. In the old days, a researcher would cut a large protein into fragments and assign each fragment, typically 10 or so amino acids long, to a graduate student for analysis. One of the fundamental pieces of information concerning a protein is the primary structure or sequence of amino acids. Within the red cell, hemoglobin S has reduced affinity for oxygen, compared with hemoglobin A, because of competition between polymerization and oxygen binding.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
